The sleeping position we adopt significantly influences our health and well-being. Although sleeping on our side is common, it’s essential to consider its potential negative effects and explore more beneficial alternatives.
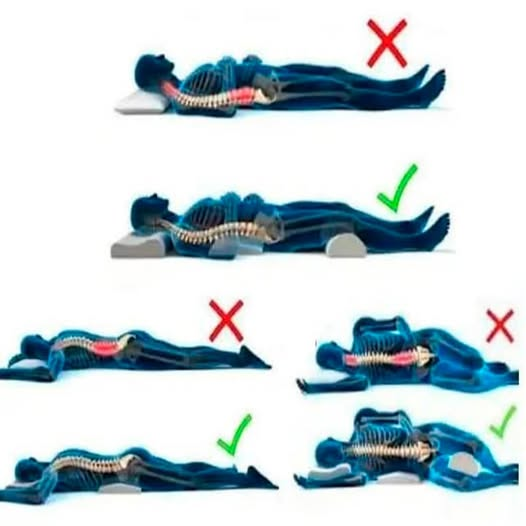
Below, all the information we need for our well-being.
Impact of sleeping on your side
- Spinal misalignment : Sleeping on your side, especially in a hunched position, can misalign your spine, putting uneven pressure on your intervertebral discs. This can lead to neck and back pain, especially if your mattress and pillow don’t provide adequate support.
- Appearance of wrinkles and sagging : Constant contact of one side of the face with the pillow can accelerate the formation of wrinkles and contribute to the loss of skin elasticity, promoting facial sagging.
- Respiratory and digestive problems : Sleeping on your right side can compress your lungs and affect breathing. This position can also promote gastric reflux due to the position of the stomach and esophagus, which facilitates the rise of gastric acids.
- Pressure on internal organs : When sleeping on your side, organs such as the liver and lungs may be under additional pressure, which could hinder their proper functioning in the long term.
Recommendations for an optimal sleeping posture
- Sleeping on your back : This position helps keep your spine aligned and reduces pressure on your joints. To improve comfort and support:
- Use a medium-firm pillow that keeps your head aligned with your neck.
- Place a pillow under your knees to maintain the natural curve of your lower back and reduce lower back strain.
- Side Sleeping with Adjustments : If you prefer to sleep on your side, consider the following adjustments to minimize potential negative effects:
- Use a firm, thick pillow that keeps your head and neck aligned with your spine.
- Place a pillow between your legs to keep your hips aligned and reduce pressure on your lower back.
- Avoid sleeping on your stomach : This position can increase pressure on your spine and force your neck into an awkward rotation, which could cause discomfort and pain.
Additional tips to improve sleep quality:
- Maintain a regular sleep routine : Going to bed and getting up at the same time every day helps regulate your biological clock and improves the quality of your rest.
- Create a sleep-friendly environment : Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and at a comfortable temperature. Consider using eye masks and earplugs if necessary.
- Limit the use of electronic devices before bed : Exposure to blue light from screens can interfere with melatonin production, making it difficult to fall asleep.
- Perform relaxation exercises : Practicing techniques such as deep breathing or yoga can help reduce stress and prepare your body for a restful night’s sleep.
Adopting a proper sleeping position and following these tips can significantly contribute to improving sleep quality and, consequently, overall health.


